Difference between revisions of "Non-Empty Mosaic theorem (Barseghyan-2015) Reason1"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Izzy Friesen (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{Reason |Conclusion=Non-Empty Mosaic theorem (Barseghyan-2015) |Title=Deduction of the Non-Empty Mosaic theorem |Premises=The Second Law (Barseghyan-2015), The Third Law (Bar...") |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|Title=Deduction of the Non-Empty Mosaic theorem | |Title=Deduction of the Non-Empty Mosaic theorem | ||
|Premises=The Second Law (Barseghyan-2015), The Third Law (Barseghyan-2015) | |Premises=The Second Law (Barseghyan-2015), The Third Law (Barseghyan-2015) | ||
| + | |Formulation Text= | ||
|Diagram File=Non-empty-mosaic-theorem.jpg | |Diagram File=Non-empty-mosaic-theorem.jpg | ||
|Authors List=Hakob Barseghyan | |Authors List=Hakob Barseghyan | ||
|Formulated Year=2015 | |Formulated Year=2015 | ||
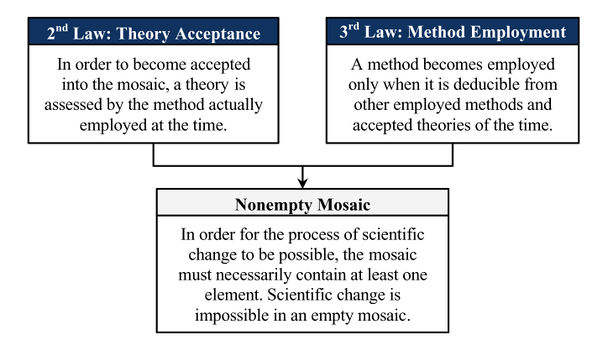
| − | |Description=Scientific change is impossible in an empty mosaic. It can be deduced from the second law, which asserts that in order to become accepted into the mosaic, a theory is assessed by the method actually employed at the time, and the third law, which asserts that a method becomes employed only when it is deducible from other employed methods and accepted theories of the time.[[ | + | |Description=Scientific change is impossible in an empty mosaic. It can be deduced from the second law, which asserts that in order to become accepted into the mosaic, a theory is assessed by the method actually employed at the time, and the third law, which asserts that a method becomes employed only when it is deducible from other employed methods and accepted theories of the time.[[CiteRef::Barseghyan (2015)|p. 226]] |
| + | |||
| + | {{PrintDiagramFile|diagram file=Non-empty-mosaic-theorem.jpg}} | ||
|Resource=Barseghyan (2015) | |Resource=Barseghyan (2015) | ||
|Page Status=Stub | |Page Status=Stub | ||
|Editor Notes= | |Editor Notes= | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 10:46, 17 January 2024
Scientific change is impossible in an empty mosaic. It can be deduced from the second law, which asserts that in order to become accepted into the mosaic, a theory is assessed by the method actually employed at the time, and the third law, which asserts that a method becomes employed only when it is deducible from other employed methods and accepted theories of the time.1p. 226
This reason for Non-Empty Mosaic theorem (Barseghyan-2015) was formulated by Hakob Barseghyan in 2015.1