Difference between revisions of "Dogmatism No Theory Change theorem (Barseghyan-2015) Reason1"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Izzy Friesen (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|Title=Deduction of the Dogmatism No Theory Change theorem | |Title=Deduction of the Dogmatism No Theory Change theorem | ||
|Premises=The First Law (Barseghyan-2015), The Second Law (Barseghyan-2015), The Third Law (Barseghyan-2015) | |Premises=The First Law (Barseghyan-2015), The Second Law (Barseghyan-2015), The Third Law (Barseghyan-2015) | ||
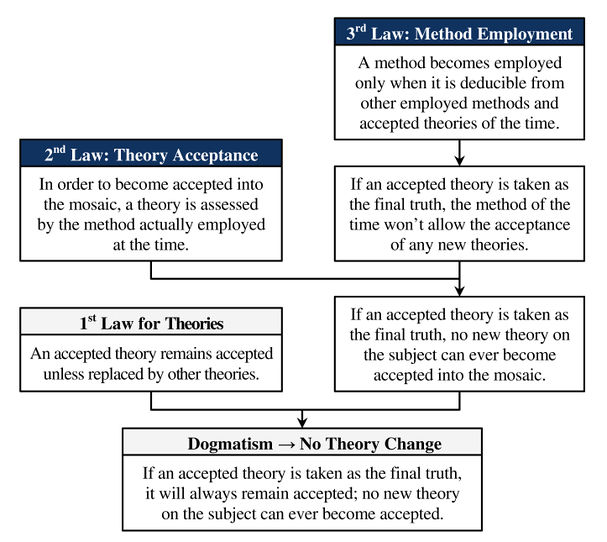
| + | |Formulation Text=The ''dogmatism no theory change'' theorem is a deductive consequence of the first law, the second law, and the third law. | ||
|Diagram File=Dogmatism-theorem.jpg | |Diagram File=Dogmatism-theorem.jpg | ||
|Authors List=Hakob Barseghyan | |Authors List=Hakob Barseghyan | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
{{PrintDiagramFile|diagram file=Dogmatism-theorem.jpg}} | {{PrintDiagramFile|diagram file=Dogmatism-theorem.jpg}} | ||
|Resource=Barseghyan (2015) | |Resource=Barseghyan (2015) | ||
| + | |Page Status=Needs Editing | ||
| + | |Editor Notes= | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 10:39, 17 January 2024
Suppose a community has an accepted theory that asserts that it is the final and absolute truth. By the Third Law we deduce the method: accept no new theories ever. By the Second Law we deduce that no new theory can ever be accepted by the employed method of the time. By the First Law, we deduce that the accepted theory will remain the accepted theory forever1p. 165-167.
This reason for Dogmatism No Theory Change theorem (Barseghyan-2015) was formulated by Hakob Barseghyan in 2015.1