Difference between revisions of "Possible Mosaic Split theorem (Barseghyan-2015) Reason1"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Izzy Friesen (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{Reason |Conclusion=Possible Mosaic Split theorem (Barseghyan-2015) |Title=Deduction of the Possible Mosaic Split theorem |Premises=The Second Law (Barseghyan-2015), The Zero...") |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|Title=Deduction of the Possible Mosaic Split theorem | |Title=Deduction of the Possible Mosaic Split theorem | ||
|Premises=The Second Law (Barseghyan-2015), The Zeroth Law (Harder-2015) | |Premises=The Second Law (Barseghyan-2015), The Zeroth Law (Harder-2015) | ||
| + | |Formulation Text=The ''possible mosaic split theorem'' follows as a deductive consequence of the second and zeroth laws. | ||
|Diagram File=Possible-mosaic-split.jpg | |Diagram File=Possible-mosaic-split.jpg | ||
|Authors List=Hakob Barseghyan | |Authors List=Hakob Barseghyan | ||
|Formulated Year=2015 | |Formulated Year=2015 | ||
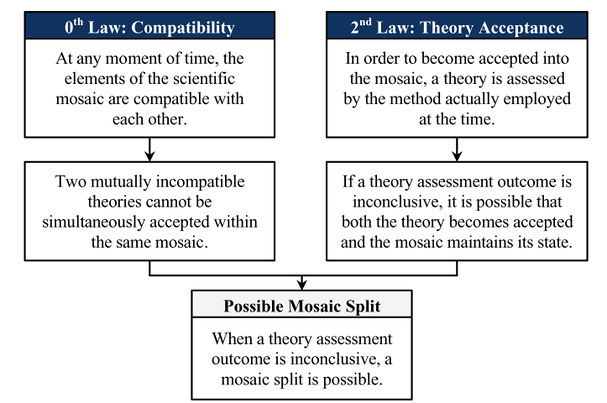
|Description=The possible mosaic split theorem follows as a deductive consequence of the second and zeroth laws, given a situation a situation where the assessment of two theories obtains an inconclusive result. This will happen when it is unclear whether or not a theory satisfies the employed method of the community. | |Description=The possible mosaic split theorem follows as a deductive consequence of the second and zeroth laws, given a situation a situation where the assessment of two theories obtains an inconclusive result. This will happen when it is unclear whether or not a theory satisfies the employed method of the community. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{PrintDiagramFile|diagram file=Possible-mosaic-split.jpg}} | ||
|Resource=Barseghyan (2015) | |Resource=Barseghyan (2015) | ||
|Page Status=Stub | |Page Status=Stub | ||
|Editor Notes= | |Editor Notes= | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:43, 17 January 2024
The possible mosaic split theorem follows as a deductive consequence of the second and zeroth laws, given a situation a situation where the assessment of two theories obtains an inconclusive result. This will happen when it is unclear whether or not a theory satisfies the employed method of the community.
This reason for Possible Mosaic Split theorem (Barseghyan-2015) was formulated by Hakob Barseghyan in 2015.1
References
- ^ Barseghyan, Hakob. (2015) The Laws of Scientific Change. Springer.