Scientonomic Workflow (Barseghyan et al.-2016)
This is an answer to the question Scientonomic Workflow that states "Scientonomic knowledge is best advanced by:
- documenting the body of accepted communal knowledge in an online encyclopedia;
- scrutinizing this accepted knowledge, identifying its flaws, and formulating open questions at seminars, conferences, publications, and other in-person or online formats;
- publishing journal articles that propose modifications to our current knowledge and documenting these suggestions;
- evaluating the suggested modifications with the goal of reaching a communal consensus and changing the respective encyclopedia pages when a verdict is reached."
Scientonomic Workflow was formulated by Nicholas Overgaard, Hakob Barseghyan, Gregory Rupik and Paul Patton in 2016.1 It is currently accepted by Scientonomy community as the best available answer to the question.
Contents
Scientonomic History
Acceptance Record
| Community | Accepted From | Acceptance Indicators | Still Accepted | Accepted Until | Rejection Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scientonomy | 1 January 2016 | This is when the implementation of the workflow by the scientonomy community began. | Yes |
Question Answered
Scientonomic Workflow (Barseghyan et al.-2016) is an attempt to answer the following question: How should changes in the accepted body of scientonomic knowledge be introduced? What are the steps and procedures of the scientonomic workflow?
See Scientonomic Workflow for more details.
Description
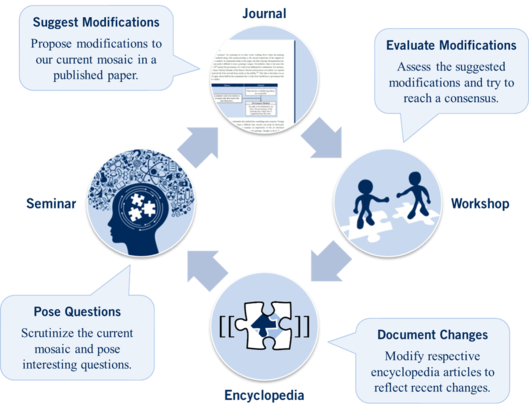
The key stages of the workflow are:
- Pose Questions: The goal of this stage is to scrutinize the current state of the scientonomic theory and our knowledge of scientific change and identify as many open questions as possible. The annual seminar on scientonomy hosted by the University of Toronto's Institute for the History and Philosophy of Science and Technology is currently the main venue facilitating this stage of the workflow.
- Suggest Modifications: The goal of this stage is to advance our knowledge of scientific change by proposing modifications to our current body of knowledge. These suggested modifications are published and properly documented. These modifications are currently published in the Journal of Scientonomy but, in principle, they can be published in any journal which makes use of the scientonomic mechanism of modifications. Once a modification is published, this encyclopedia documents that suggestions and invites experts to review it.
- Evaluate Modifications: The goal of this stage is to assess the suggested modifications and decide which of them are acceptable and which are not. This is done by the community of scientonomists on the respective discussion pages of this encyclopedia. If a consensus emerges, the fate of the modification is documented. If a modification causes disagreement among scientonomists, it becomes a topic of discussion during scientonomic workshops, which aim at bridging the gaps between opposing parties and arriving at consensus.
- Document Changes: The goal of this stage is to document all the changes in our communal body of knowledge. If a modification is considered acceptable by the community, then the respective articles of this encyclopedia are modified to reflect that change. If a modification is considered unacceptable, then the respective verdict is documented for that modification.
The primary role of this encyclopedia in the scientonomic workflow is to document the current state of scientonomic knowledge, trace all suggested modifications, and list open questions.
Here is an outline of the main stages of the scientonomic workflow:
This workflow gives researchers a simple way of knowing where the community stands on different topics, i.e. what theories it currently accepts, what open questions it tries to answer, what modifications have been proposed and how they have been assessed. It ensures that our communal knowledge is advanced in a piecemeal and transparent fashion:
- Piecemeal: modifications to the communal mosaic are suggested one by one, which allows for a sober critical evaluation of these suggestions by the community.
- Transparent : suggested modifications and their evaluations are properly documented, so that there is no mystery as to whether, when, or why a certain modification was or wasn't accepted.
The workflow is scalable, as it can - in principle - be implemented in other fields of digital humanities and beyond.
Reasons
No reasons are indicated for this theory.
If a reason supporting this theory is missing, please add it here.
Questions About This Theory
There are no higher-order questions concerning this theory.
If a question about this theory is missing, please add it here.
References
- ^ Shaw, Jamie and Barseghyan, Hakob. (2019) Problems and Prospects with the Scientonomic Workflow. Scientonomy 3, 1-14. Retrieved from https://scientojournal.com/index.php/scientonomy/article/view/33509.