Difference between revisions of "Mechanism of Question Rejection"
(Created page with "{{Topic |Question=What is the mechanism of question rejection? How do questions become rejected by epistemic agents? |Topic Type=Descriptive |Description=Question rejection is...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Topic | {{Topic | ||
| − | |Question | + | |Subject=Question |
|Topic Type=Descriptive | |Topic Type=Descriptive | ||
| + | |Subfield=Dynamics | ||
| + | |Inherited From= | ||
| + | |Heritable=Yes | ||
| + | |Question Text Formula=How do <subjects> become rejected? What is the mechanism of <subject> rejection? | ||
| + | |Question Title Formula=Mechanism of <Subject> Rejection | ||
| + | |Question= | ||
| + | |Question Title= | ||
| + | |Predicate=mechanism of rejection | ||
| + | |Object Type=Text | ||
| + | |Object Value True= | ||
| + | |Object Value False= | ||
| + | |Object Class= | ||
| + | |Object Enum Values= | ||
| + | |Object Regexp= | ||
| + | |Single Answer Text Formula= | ||
| + | |Multiple Answers Text Formula= | ||
| + | |Answer Title Formula= | ||
|Description=Question rejection is an integral part of question dynamics. As some questions become accepted, others become rejected by epistemic agents. Thus, it is important to unearth the underlying dynamics of question rejection. | |Description=Question rejection is an integral part of question dynamics. As some questions become accepted, others become rejected by epistemic agents. Thus, it is important to unearth the underlying dynamics of question rejection. | ||
|Parent Topic=Mechanism of Scientific Change | |Parent Topic=Mechanism of Scientific Change | ||
| Line 11: | Line 28: | ||
|Current View= | |Current View= | ||
|Page Status=Stub | |Page Status=Stub | ||
| − | |Editor Notes= | + | |Editor Notes= |
}} | }} | ||
{{Acceptance Record | {{Acceptance Record | ||
Revision as of 23:24, 2 January 2024
How do questions become rejected? What is the mechanism of question rejection?
Question rejection is an integral part of question dynamics. As some questions become accepted, others become rejected by epistemic agents. Thus, it is important to unearth the underlying dynamics of question rejection.
In the scientonomic context, this question was first formulated by Hakob Barseghyan and Nichole Levesley in 2021. The question is currently accepted as a legitimate topic for discussion by Scientonomy community.
In Scientonomy, the accepted answer to the question is:
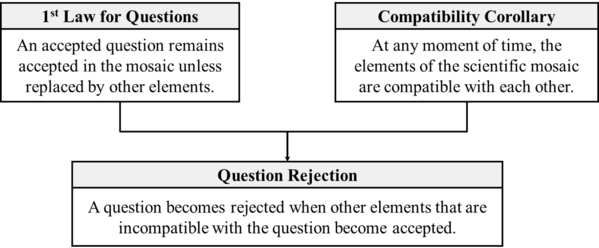
- A question becomes rejected when other elements that are incompatible with the question become accepted.
Contents
Scientonomic History
Acceptance Record
| Community | Accepted From | Acceptance Indicators | Still Accepted | Accepted Until | Rejection Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scientonomy | 1 August 2021 | This is when Barseghyan and Levesley's Question Dynamics that offered an answer to the question was published. This is a good indication that the question itself is considered legitimate by the community. | Yes |
All Theories
| Theory | Formulation | Formulated In |
|---|---|---|
| Question Rejection theorem (Barseghyan-Levesley-2021) | A question becomes rejected when other elements that are incompatible with the question become accepted. | 2021 |
| Question Rejection theorem (Barseghyan-Levesley-Pandey-2023) | A question becomes rejected when other elements that are incompatible with the question become part of the mosaic. | 2023 |
If an answer to this question is missing, please click here to add it.
Accepted Theories
| Community | Theory | Accepted From | Accepted Until |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scientonomy | Question Rejection theorem (Barseghyan-Levesley-2021) | 21 February 2024 |
Suggested Modifications
| Modification | Community | Date Suggested | Summary | Verdict | Verdict Rationale | Date Assessed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sciento-2021-0002 | Scientonomy | 1 August 2021 | Accept the law of question acceptance as a new scientonomic axiom, the question rejection theorem, and a number of questions for future research. | Accepted | Prior to the 2024 workshop, Carlin Henikoff left a comment on the encyclopedia affirming that the modification should be accepted, but also stating that it was unclear whether it should be accepted as an axiom, per se. During the 2024 workshop, it was clarified that in our taxonomy, if X follows from something else, it is a theorem, but if not, it is an axiom. At the time of the publication of Levesley and Barseghyan’s paper, Henikoff was engaged in conversations in the scientonomy community about whether the law of question acceptance could be deducible from other scientonomic theorems. This clarified the thrust of her comment; since the law hasn't been shown to follow from any other scientonomic theories, it can only be taken as an axiom. There were also concerns about the phrasing of the law. Specifically, Jamie Shaw highlighted that the acceptance of a question cannot be predicated upon the acceptance of all of its presuppositions, simply because a question can have an infinite number of presuppositions. However, the participants were reminded of the difference between epistemic presuppositions and logical presuppositions (proposed by Levesley and Barseghyan in the previously accepted modification Sciento-2021-0001). While a question can have an infinite number of logical presuppositions (i.e. these are “explosive”), the law explicitly talks about epistemic presuppositions, which are not explosive. The modification was accepted nearly unanimously by over two-thirds majority of votes. 17 out of 18 votes were for acceptance. | 21 February 2024 |
| Sciento-2023-0002 | Scientonomy | 28 December 2023 | Accept new formulations of the first law for theories, norms, and questions that are in tune with the formulation of the first law. Also accept new formulations of the respective rejection theorems - theory rejection, norm rejection, and question rejection. | Open |
Current View
In Scientonomy, the accepted answer to the question is Question Rejection theorem (Barseghyan-Levesley-2021).
Question Rejection theorem (Barseghyan-Levesley-2021) states: "A question becomes rejected when other elements that are incompatible with the question become accepted."
Similar to other scientonomic rejection theorems, the question rejection theorem assumes that questions become rejected as they get pushed out of an agent's mosaic due to their incompatibility with some newly accepted elements. There are two most common scenarios of such incompatibility.
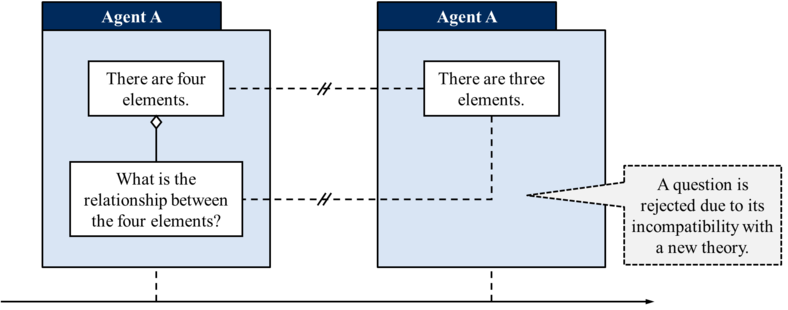
In the first scenario, a question becomes rejected due to the acceptance of a new theory that happens to be incompatible with some of the question's epistemic presuppositions. As explained by Barseghyan and Levesley:
imagine an epistemic situation where agent A initially accepts the question “What is the relationship between the four elements?” together with the theoretical presupposition that there are four elements. Suppose also that at some later time the agent discovers that there are not four but three elements. Naturally, the agent rejects both the theory of four elements and the question about the relationships between these elements:
Importantly, this rejection happens regardless of whether it ever occurs to the agent to ask a new question “What is the relationship between the three elements?”. Even if the agent never accepts any further questions concerning the three elements, the question “What is the relationship between the four elements?” would still be rejected.1pp. 14-15
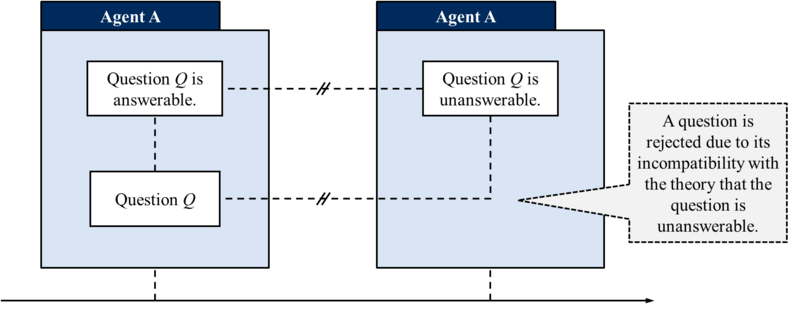
In the second scenario, a question is being rejected due to the acceptance of the second-order theory stating that the question is unanswerable (the latter being incompatible with the question). In the words of Barseghyan and Levesley:
Consider [an] epistemic situation, where agent A accepts some question Q, together with the theory that Q is answerable. When agent A comes to accept that Q is unanswerable, the agent rejects question Q. The scientonomic mechanism of this rejection is through the incompatibility of question Q and the theory “Question Q is unanswerable”:1p. 15
Related Topics
This question is a subquestion of Mechanism of Scientific Change.
References
- a b Barseghyan, Hakob and Levesley, Nichole. (2021) Question Dynamics. Scientonomy 4, 1-19. Retrieved from https://scientojournal.com/index.php/scientonomy/article/view/37120.