Modification:Sciento-2018-0006
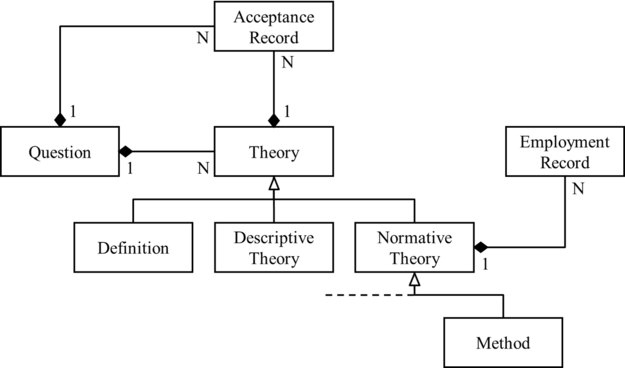
Accept the new ontology of epistemic elements with, theories and questions are the two basic epistemic elements where and each theory is an attempt to answer a certain question, theories can be of three types – descriptive, normative, or definitions, and methods are a subtype of normative theory.
The modification was suggested to Scientonomy community by Hakob Barseghyan on 8 October 2018.1 The modification was accepted on 1 September 2019.
Contents
Preamble
The current scientonomic ontology is flawed in a number of ways. First, it doesn’t include definitions as a subtype of theory and, therefore, differs from the ontology that is in the backbone of the Encyclopedia of Scientonomy. In addition, it distinguishes between two classes of elements – methods and methodologies – based on their respective historical fates rather than their propositional contents. This results in a somewhat absurd practice when the same criterion of theory evaluation can be classified either as a theory (methodology) or as a method depending on whether it has or hasn’t been historically accepted and/or employed. Furthermore, the currently accepted ontology relies heavily on the distinction between implicit and tacit, whereas the analysis shows that implicitness or explicitness cannot be grounds for drawing ontological distinctions. Consequently, we need to accept a new scientonomic ontology which doesn’t confuse the propositional content of an element with the historical records of its acceptances and/or employments.
The suggested ontology helps solve some of the issues permeating the current ontology. First, it builds on Rawleigh’s suggestion to include questions as a distinct class of epistemic elements and considers a theory as an attempt to answer a certain question. Second, since method is defined as a set of criteria for theory evaluation, it is not an independent epistemic element but is a subtype of normative theory. Third, since methods and methodologies of the currently accepted ontology do not differ from the perspective of their propositional content (i.e. both are criteria for theory evaluation), they in fact belong to one and the same class of epistemic elements. I suggested to reserve the word “method” for this type of epistemic element, and use “methodology” to denote the respective normative discipline. Fourth, it stipulates that methods can be both accepted and employed. However, it notes that the ability of being employed is not peculiar exclusively to methods, but characterizes normative propositions of all kinds, including ethical norms, aesthetic norms, and technological guidelines. Fifth, it introduces definition as a subtype of theory.
Modification
Accept the following ontology:
Theories To Accept
- Theory Acceptance (Barseghyan-2018): A theory is said to be accepted by an epistemic agent if it is taken as the best available answer to its respective question.
- Theory Answers Question (Rawleigh-2018): A theory is an answer to a question.
- Definition Is a Subtype of Theory (Barseghyan-2018): Definition is a subtype of Theory, i.e. theory is a supertype of definition.
- Method Is a Subtype of Normative Theory (Barseghyan-2018): Method is a subtype of Normative Theory, i.e. normative theory is a supertype of method.
- Norm Employment Is a Subtype of Epistemic Stance (Barseghyan-2018): Norm Employment is a subtype of Epistemic Stance, i.e. epistemic stance is a supertype of norm employment.
- Norm Employment Exists: There is such a thing as norm employment.
- Epistemic Stances Towards Normative Theories - Norm Employment (Barseghyan-2018): The stance of norm employment can be taken towards a normative theory.
- Definition Exists: There is such a thing as a definition.
Theories To Reject
- Theory Acceptance (Sebastien-2016): A theory is said to be accepted if it is taken as the best available description or prescription of its object.
- Method Is a Subtype of Epistemic Element (Barseghyan-2015): Method is a subtype of Epistemic Element, i.e. epistemic element is a supertype of method.
Questions To Accept
- Role of Definitions in Scientific Change: Do definitions play any distinct role in the process of scientific change, or do they only exhibit the exact same patterns as descriptive and normative theories?
- Reducibility of Definitions: Are definitions somehow reducible to other epistemic elements, such as descriptive or normative theories?
Questions Answered
This modification attempts to answer the following question(s):
- Epistemic Stances Towards Normative Theories: What types of epistemic stances can be taken by epistemic agents towards normative theories?
- Theory Acceptance: What does it mean to say that a theory is accepted? How should theory acceptance be defined?
- Supertypes of Method: What are the supertypes of a method?
- Subtypes of Theory: What are the subtypes of a theory?
- Associations of Theory: How is the class of theory associated with other classes (and itself)? What aggregation, composition, or other association relations can exist between theories, as well as between a theory and instances of other classes?
- Associations of Question: How is the class of question associated with other classes (and itself)? What aggregation, composition, or other association relations can exist between questions, as well as between a question and instances of other classes?
- Subtypes of Normative Theory: What are the subtypes of a normative theory?
- Supertypes of Definition: What are the supertypes of a definition?
- Subtypes of Epistemic Stance: What are the subtypes of an epistemic stance?
- Supertypes of Norm Employment: What are the supertypes of norm employment?
- Existence of Norm Employment: Does norm employment exist?
- Existence of Definition: Does a definition exist?
Verdict
The modification was accepted on 1 September 2019. Following a series of off-line discussions, a consensus emerged concerning this modification: it was agreed that the modification is to be accepted.c1 It was mentioned that most of the elements of this new ontology "has already been accepted by the scientonomic community".c2 It was also stressed that "the consensus has been manifested on several occasions, including the first scientonomy conference in May 2019 in Toronto, where several of the presenters treated this new ontology as accepted."c3 The fact that the consensus concerning this modification has been achieved primarily off-line, i.e. outside of the discussion pages of this encyclopedia suggests that the scientonomic "workflow must have a way of accommodating these discussions".c4
Click on the Discussion tab for comments.
References
- ^ Barseghyan, Hakob. (2018) Redrafting the Ontology of Scientific Change. Scientonomy 2, 13-38. Retrieved from https://scientojournal.com/index.php/scientonomy/article/view/31032.